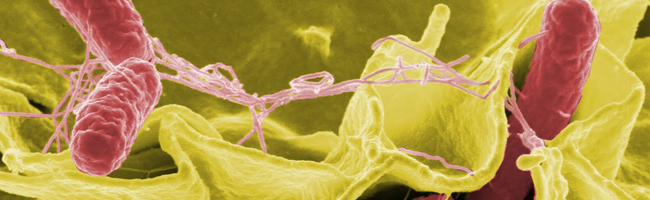
Harmful Antibiotic-Resistant Superbugs Found in Meat
Meat is a hot topic, as more and more people are opting for “Meatless Mondays” and even dropping the protein staple from their diets, discovering TVP (textured vegetable protein) and restaurant chains like Native Foods Cafe, Hugo’s Tacos and even Chipotle, offering tasty non meat options.
If there was ever a reason to ditch animal flesh, a new study has revealed superbugs, thanks to antibiotic misuse in animals, are on the rise.
More people find that you can get all the protein you need from plant-based sources. For the hold outs who still love a good steak or chicken breast, you have to become extra vigilant in your handling and purchasing of meat.
In February, the National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (NARMS) released its annual report on retail meat. The results were alarming. The Environmental Working Group (EWG) analyzed the findings on samples of poultry, pork, and beef, and concluded that there were antibiotic-resistant salmonella and Campylobacter bacteria on:
- 81 percent of ground turkey
- 69 percent of pork chops
- 55 percent of ground beef
- 39 percent of chicken breasts, wings, or thighs
Salmonella and Campylobacter superbug versions limit the possible medications that will be effective in treatment, meaning a possible hospital stay or even chronic arthritis from salmonella complications. According to EWG, Campylobacter can result in Guillan-Barre Syndrome, an autoimmune disorder that could leave you paralyzed. Severe cases in immunity-compromised individuals are fatal.
The EWG report states that 53 percent of the chicken samples contained superbug versions of E.coli bacteria, which can cause severe diarrhea, vomiting, fever and worse.
You can thank the misuse of antibiotics in livestock for this proliferation of superbugs. Livestock are given antibiotics in order to promote rapid growth and maintain their health even in cramped and unsanitary conditions. For those of you in southern California, if you have ever driven on I-5 through Coalinga, you see (and smell) unhappy cows standing in their own filth, confined in limited space being fed corn to fatten up quickly. More antibiotics are given to animals than humans according to Dr. Gail Hansen, a veterinarian and senior officer for the Pew Campaign on Human Health and Industrial Farming, a project aimed at phasing out overuse of antibiotics in food production. She says, “Antibiotic use in animals is out of hand. We feed antibiotics to sick animals, which is completely appropriate, but we also put antibiotics in their feed and in their water to help them grow faster and to compensate for unhygienic conditions. If you have to keep the animals healthy with drugs, I would argue you need to re-examine the system. You don’t take antibiotics preventively when you go out into the world.”
According to CNN, the FDA is collaborating with the meat industry to cut back on unnecessary antibiotic use in animals. The FDA doesn’t track how the antibiotics they purchase are actually put to use, so good luck finding this information from a credible source.
What to do to mitigate the issue:
Cook meat with a meat thermometer to make sure your food is thoroughly heated, and be vigilant about washing your hands, not re-using utensils, and cleaning up when you’re done in the kitchen.
Remember that all meat you consume has chemicals, hormones, and even steroids possibly, so try to cut down on your meat consumption.
If you eat meat, make sure you buy organic, hormone-free animal products. If you can, buy from a known source whose animals are ethically raised and slaughtered.
Try alternatives to meat such as fish a few times a week, and choose wild Alaskan salmon, mahi-mahi, sole, tilapia, striped sea bass, haddock, and halibut over the ones that are higher in toxins, like swordfish, tuna, shark, bluefish and Chilean sea bass.
Grains and veggies have protein!
Quinoa is a grain that is high in protein. Green vegetables like Broccoli have 11.2 grams of protein per 100 calories whereas steak only has 5.4 grams.
Raw hemp protein powder and hemp seeds are superior powdered protein mix alternatives for smoothies and drinks with 11 grams of protein per 30-gram serving.
Source(s)
I. National Antimicrobial Resistance MOnitoring System, FDA (04/2013)
II. Superbugs, Environmental Working Group (04/2013)
III. Turkey, Consumer Reports (04/2013)
IV. Tests Find Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria In Raw Meat, Fox 5 (04/2013)